Theme: COPD Today: Clinical and Research Issues
Copd 2018
Conference Series Ltd is overwhelmed to announce the commencement of “6th International Conference on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease” to be held during May 17-18, 2018 in Tokyo, Japan. The upcoming conference will be organized around the theme " COPD Today: Clinical and Research Issues".
Conference Series Ltd organizes 1000+ Conferences every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
COPD 2018 Conference brings together individuals who have an interest in the field of Respiratory and Pulmonary Disease relating to diversified topics like COPD, emphysema, asthma, cystic fibrosis, lung cancer, other pulmonary diseases and therapeutics. It is a forum to explore issues of mutual concern as well as exchange knowledge, share evidence and ideas, and generate solutions.
Target Audience:
This event is suited to anyone with an academic or professional interest in COPD and its research; including Researchers, Senior scientists, Pulmonologists, Professors, Doctors, Nurses, Healthcare Professionals, Pharmacologists, Clinicians, Directors of Association and Societies, Postgraduate students and those who work in research and development of pharmaceuticals and related technology.
Why to Attend???
COPD 2018 conference is an opportunity to meet others within speciality to network and to learn the latest clinical information.
With members from around the world focused on learning about pulmonary care and its advances; this is your best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the Respiratory community. Conduct presentations, distribute information, meet with current and potential scientists, make a splash with new discoveries in the COPD treatment and diagnosis, and receive name recognition at this 2-day event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, developments, and the newest updates in the world of Respiratory care are hallmarks of this conference.
Scope and Importance:
Pulmonary health has a particular interest on the impact changes in respiratory care and the awareness is increasing every year, and therefore COPD 2018 encourages submissions from researchers based in USA, Europe and Asian countries.
The challenge of the field is to evaluate current promising interventions rigorously, address emerging issues such as synthesizing ever-increasing research findings, and develop innovative dissemination and communication strategies.
The journal invites submissions on research in COPD, including emphysema, tuberculosis, asthma, pulmonary rehabilitation, cystic fibrosis, lung cancer and topics related to respiratory health.
COPD 2018 provides a platform that helps authors to share their knowledge with a wider audience, and sustains a rapid process for submissions resulting in high quality publications. We further aim to contribute towards reducing the inequity in publications from low- and middle-income countries. Our audience is global and we intend to share research results in COPD from all parts of the world.
Track 1: Pathogenesis of COPD
The diseases that fall under the scope of COPD are: Chronic Bronchitis, Emphysema and COPD-Asthma overlap. Chronic Bronchitis causes inflammation and irritation of the airways, the tubes in your lungs where air passes through. When the air tubes are inflamed and irritated, thick mucus begins to form in them. Over time, this mucus plugs up airways and makes breathing difficult. When you cough this mucus up, the excretions are known as sputum, or phlegm. Emphysema is a common type of COPD in which the air sacs of the lungs become damaged, causing them to enlarge and burst. Damage in this area makes it difficult for people with emphysema to expel air from their lungs. This leads to a build-up of carbon dioxide in the body and a myriad of emphysema signs and symptoms. Asthma COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) is usually characterized by increased reversibility of airflow obstruction, eosinophilic bronchial and systemic inflammation, and increased response to inhaled corticosteroids, compared with COPD patients. The relevance of the ACOS is the need to identify patients with COPD who may have underlying eosinophilic inflammation that responds better to inhaled corticosteroids. Until new diagnostic tools are developed, a previous diagnosis of asthma in a patient with COPD can be a reliable criterion to suspect ACOS in a patient with COPD.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 2: CO-Morbidities in COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to a collection of lung diseases that can lead to blocked airways. People with COPD can be at risk for some serious complications that can not only put their health in jeopardy, but can also fatal. In COPD patients, Pneumonia occurs when bacteria enter the lungs, creating an infection. For COPD patients, pneumonia can weaken the lungs. This can lead to a chain reaction of illnesses that can weaken the lungs even further. This downward spiral can lead to a rapid deterioration of health in COPD patients. Respiratory Insufficiency is an important complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This may represent deterioration in the patient's premorbid condition such that hypoxemia worsens and hypercapnia develops during a relatively trivial respiratory tract infection, which may be viral or bacterial, Alternatively, these changes may occur for the first time in someone with less severe COPD who encounters a particularly dramatic cause for deterioration, e.g. lobar pneumonia or acute pulmonary oedema. Pneumothorax is defined as the accumulation of air or gas in the space between the lung and the chest wall. Also known as a collapsed lung, pneumothorax occurs when a hole develops in the lung that allows air to escape in the space around the lung, causing the lungs to partially or completely collapse. People with COPD, are at greater risk for pneumothorax because the structure of their lungs is weak and vulnerable to the spontaneous development of these types of holes. Pneumo mediastinum must be differentiated from spontaneous pneumothorax. Patients may or may not have symptoms, as this is typically a well-tolerated disease, although mortality in cases of esophageal rupture is very high.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 3: Asthma and allergy
Asthma is a long-term respiratory condition caused by hypersensitivity and inflammation of the airways. Symptoms include a cough, wheezing, chest tightness and breathlessness, and can vary in severity from person to person. When asthma symptoms get significantly worse, it is known as an 'asthma attack'.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 4: Lung Diseases
The term lung disease refers to many disorders affecting the lungs, such as asthma, COPD, infections like influenza, pneumonia and tuberculosis, lung cancer, and many other breathing problems. Some lung diseases can lead to respiratory failure.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 5: Epidemology of COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to a collection of lung diseases that can lead to blocked airways. People with COPD can be at risk for some serious complications that can not only put their health in jeopardy, but can also fatal. In COPD patients, Pneumonia occurs when bacteria enter the lungs, creating an infection. For COPD patients, pneumonia can weaken the lungs. This can lead to a chain reaction of illnesses that can weaken the lungs even further. This downward spiral can lead to a rapid deterioration of health in COPD patients. Respiratory Insufficiency is an important complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This may represent deterioration in the patient's premorbid condition such that hypoxemia worsens and hypercapnia develops during a relatively trivial respiratory tract infection, which may be viral or bacterial, Alternatively, these changes may occur for the first time in someone with less severe COPD who encounters a particularly dramatic cause for deterioration, e.g. lobar pneumonia or acute pulmonary oedema. Pneumothorax is defined as the accumulation of air or gas in the space between the lung and the chest wall. Also known as a collapsed lung, pneumothorax occurs when a hole develops in the lung that allows air to escape in the space around the lung, causing the lungs to partially or completely collapse. People with COPD, are at greater risk for pneumothorax because the structure of their lungs is weak and vulnerable to the spontaneous development of these types of holes. Pneumo mediastinum must be differentiated from spontaneous pneumothorax. Patients may or may not have symptoms, as this is typically a well-tolerated disease, although mortality in cases of esophageal rupture is very high.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 6: COPD Theraupetics
The symptoms of COPD cannot be completely eliminated with treatment and the condition usually worsens over time. However, treatment can control symptoms and can sometimes slow the progression of the disease. Medications that help open the airways, called bronchodilators, are a mainstay of treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Bronchodilators help to keep airways open and possibly decrease secretions. Short-acting anticholinergic medication (ipratropium, Atrovent) improves lung function and symptoms. If symptoms are mild and infrequent, short-acting anticholinergic medication may be recommended only when you need it, and Long-acting beta agonists may be recommended if your symptoms are not adequately controlled with other treatments. Glucocorticoids taken in pill form or as an injection are sometimes used for short term treatment but are not generally used long-term because of the risk of side effects. Several such combinations are available including fluticasone proprionate/salmeterol (Advair) and budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort), which are taken twice daily, and fluticasone furoate/vilanterol (Breo), which is taken once daily. People with advanced COPD can have low oxygen levels in the blood. This condition, known as hypoxemia and the oxygen level can be measured with a device placed on the finger or with a blood test (arterial blood gas). Fatal fires have occurred in people attempting to smoke while using oxygen. Unintended weight loss caused by shortness of breath usually occurs in people with more advanced lung disease. Not eating enough can lead to malnutrition, which can make symptoms worse and increase the likelihood of infection. Other treatments for COPD are including Noninvasive ventilatory support (the use of a special mask and breathing machine to improve symptoms), anti-anxiety or anti-depressant medications, or morphine-like medications to reduce shortness of breath.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 7: COPD Exacerbations
An acute exacerbation of COPD is a flare-up or episode when your breathing gets worse than usual and you become sick. It is most often linked to an infection. Exacerbations are often linked to a lung infection that results from a virus or bacteria, like a cold or some other illness. Spending time in smoggy or dirty air can also make your symptoms get worse quickly. Exacerbations Management may be accompanied by increased amount of cough and sputum productions, and a change in appearance of sputum. An abrupt worsening in COPD symptoms may cause rupture of the airways in the lungs, which in turn may cause a spontaneous pneumothorax. Preventing acute exacerbations Management helps to reduce long-term complications. Long-term oxygen therapy, regular monitoring of pulmonary function and referral for pulmonary rehabilitation are often indicated. Influenza and pneumococcal vaccines should be given. Patients who do not respond to standard therapies may benefit from surgery. Pulmonary Rehabilitations a programme of exercise and education for people with long-term lung conditions help to improve your muscle strength, so you can use the oxygen you breathe more efficiently, improve your general fitness and help you to cope better with feeling out of breath and also help you to feel to stronger and fitter, and able to do more PR is about helping you manage your condition better. It is not a cure, but you will feel better and more confident and in control. PR requires your commitment to really work. People who learn about their COPD and treatment plan are better able to recognize symptoms and take appropriate action. However, education is no substitute for regular exercise as part of a pulmonary rehab program.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 8: Self-Management and Prevention of COPD
Self- Management interventions help patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) acquire and practise the skills they need to carry out disease-specific medical regimens, guide changes in health behaviour and provide emotional support to enable patients to control their disease. These programmes are based on the presumption that effective modification of behaviour can be attained only if patients’ self-efficacy has been improved. Patients who have enough confidence in their ability to successfully respond to certain events, such as at the time of an exacerbation, can more easily modify and maintain the desired behaviour. The behavioural modification should ultimately result in improved clinical outcomes. COPD self-management programmes have shown positive effects on patients’ quality of life and healthcare use in secondary care settings, but the benefits in general practice are still inconclusive. There are also breathing techniques that can help you get the air you need without working so hard to breathe, Our primary objective was to assess the long term effects of two different modes of COPD disease management—comprehensive self-management and routine monitoring—on quality of life in COPD patients in general practice. As secondary objectives, we assessed the effects on frequency and patients’ management of exacerbations and on self-efficacy.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 9: Management of COPD
The goal of COPD management is to improve a patient’s functional status and quality of life by preserving optimal lung function, improving symptoms, and preventing the recurrence of exacerbations. Currently, no treatments aside from lung transplantation have been shown to significantly improve lung function or decrease mortality; however, oxygen therapy (when appropriate) and smoking cessation may reduce mortality. Once the diagnosis of COPD is established, it is important to educate the patient about the disease and to encourage his or her active participation in therapy.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 10: Diagnostic Evaluation of COPD
Lung (pulmonary) function tests: Pulmonary function tests measure the amount of air inhaled and exhaled, and if your lungs are delivering enough oxygen to your blood.
Spirometry is the most common lung function test. Spirometer measures how much air lungs can hold and how fast air is blown out of your lungs. Spirometry can detect COPD even before symptoms of the disease arise. It can also be used to track the progression of disease and to monitor how well treatment is working. Spirometry often includes measurement of the effect of bronchodilator administration. Other lung function tests include measurement of lung volumes, diffusing capacity and pulse oximetry.
Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can show emphysema, one of the main causes of COPD. An X-ray can also rule out other lung problems or heart failure.
CT scan: A CT scan of lungs can help detect emphysema and help determine the need for surgery for COPD. CT scans can also be used to screen for lung cancer.
Arterial blood gas analysis: This blood test measures how well lungs are bringing oxygen into blood and removing carbon dioxide.
Laboratory tests: Laboratory tests aren't used to diagnose COPD, but they may be used to determine the cause of symptoms or rule out other conditions. For example, laboratory tests may be used to determine if you have the genetic disorder alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAt) deficiency, which may be the cause of some cases of COPD.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 11: Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs and the right side of your heart.
In one form of pulmonary hypertension, tiny arteries in your lungs, called pulmonary arterioles, and capillaries become narrowed, blocked or destroyed. This makes it harder for blood to flow through your lungs, and raises pressure within your lungs' arteries. As the pressure builds, your heart's lower right chamber (right ventricle) must work harder to pump blood through your lungs, eventually causing your heart muscle to weaken and fail.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 12: Cardiovascular Risk and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Cardiovascular disease contributes significantly to both morbidity and mortality in COPD. Shared risk factors for cardiovascular disease and COPD, such as smoking, low socioeconomic class, and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to the natural history of each of these conditions. novel mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease, and these may play an important role in driving the increased cardiovascular risk associated with COPD
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 13: Lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. This growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The two main types are small-cell lung carcinoma and non-small-cell lung carcinoma The most common symptoms are coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pains.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 14: Airway and Therapeutic Devices
In recent years patients with respiratory diseases use various devices, which help the removal of mucus from the airways and the improvement of pulmonary function. These devices seem to increase patients' compliance to daily treatment, because they present many benefits, as independent application, full control of therapy and easy use. Some of the devices are -the Positive Expiratory Pressure, the High Frequency Chest Wall Oscillation, the Oral High Frequency Oscillation, the Intrapulmonary Percussive Ventilation, the Incentive Spirometry the Flutter and the Acapella and the Cornet. Current devices seem to be effective in terms of mucus expectoration and pulmonary function improvement.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 15: Pulmonary diseases-treatment and therapies
Basing on the type of the disease, different treatments are available for chest diseases.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Track 16: Pediatric Pulmonary,Critical care and Sleep
Pediatric pulmonary study helps to provide comprehensive care to infants, children and adults with a full spectrum of respiratory disorders.comprehensive evaluation and treatment of children with acute and chronic respiratory diseases can be done with research in this field.
Related Conferences: 3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA; 6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA; 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan; 13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; 5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization
Track 17: Environmental and Occupational lung Disease
Environmental lung diseases are caused by harmful particles, mists, vapors, or gases that are inhaled, usually while people work. The emergence of novel occupational causes of respiratory disease in recent years emphasises the need for continuing vigilance.
Related Conferences: 3rd International Conference on Flu & Emerging Infectious Diseases, October 30-November 01 2017 Las Vegas, USA;3rd Annual Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs, October 30-November 1 2017 San Antonio, Texas, USA;7th Asia Pacific STD and Infectious Diseases Congress October 23-25, 2017 Osaka, Japan;6th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, May 2-3, 2018 Orlando, USA;5th International congress on Infectious diseases, March 1-2 2018 Berlin, Germany;13th World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control going to be held in Dec 14-16, 2017 Rome, Italy; Asian Pacific Society of Respirology; Chinese COPD Patient Education Organization; COPD Club of Northern Thailand; COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
Major COPD Research Associations around Asia Pacific
COPD Patient Organization of Vietnam
COPD Patients Club Kyrgyzstan
COPD Club of Northern Thailand
Asian Pacific Society of Respirology
Chinese COPD Patient Education Organziation
Major COPD Research Associations around Globe
Alpha-1 Foundation
American Association for Respiratory Care
American College of Chest Physicians
American College of Emergency Physicians
American College of Physicians
American Lung Association
Canadian Lung Association (CLA)
COPD Foundation
Target Audience:
• Directors, Board Members, Presidents, Vice Presidents, Deans and Head of the Departments
• COPD Students, Scientists, Faculty
• Medical Colleges
• COPD Associations and Societies
• Business Entrepreneurs, Pharmaceutical companies
Universities Associated with COPD 2017
Major Universities on COPD Research
Kumamoto University, Japan
Tokyo National Hospital, Japan
KindaiUniversity, Japan
Okayama University, Japan
Medi7 Bentleigh, Australia
Macquarie University, Australia
Australian national university, Australia
Charles Darwin University Casoria Australia
Curtin University Bentley, Australia
Dar Al Uloom University, Saudi Arabia
Iqbal Chest Centre, Bangladesh
Imperial College London, United Kingdom
Linnaeus University, Sweden
University Of California Los Angeles, United States
Columbia University Medical Center, United States
Harvard University, United States
Global Market research on COPD
The global COPD market is estimated to currently be worth $11.3 billion, and is forecast to reach
a value of $15.6 billion by 2019. The drugs driving this growth include once-daily LABA/LAMA
fixed-dose combinations such as QVA-149, umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol and olodaterol/tiotropium.
The opportunity in the U.S. and China asthma and COPD drugs market is slated to rise from a valuation of US$13.0 bn in 2015 to be worth US$18.7 bn by 2024. If these values hold true, the market is likely to expand at a modest CAGR of 4.1% therein.
North America leads the global market for asthma &COPD drugs and devices. North America was followed by Europe in terms of market capitalization. Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest regional market for asthma and COPD owing to the increased incidence of asthma & other respiratory diseases in industrial regions.
The current asthma and COPD market is primarily driven by increasing patient population. It is also growing due to factors such as price erosion and expiry of patents of leading drug brands in the market. However, it is estimated that in the next five years, the global asthma and COPD drug market is expected to grow slowly and steadfast. The COPD segment was projected to be worth USD 10,593.2 million and is expected to reach USD 12,619.8 million in 2017.
In Europe, LABA / ICS combinations and LTA (Montelukast) drugs are more popular for asthma
and COPD treatment.
Top few companies in this global market:
AstraZeneca
GlaxoSmithKline
F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Novartis and Merck
Abbott
Amgen
Actavis
BoehringerIngelheim
Cipla
Glenmark
Pfizer
Ranbaxy
Sunovion
Vectura
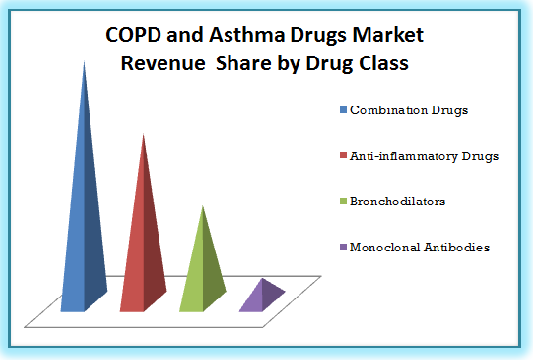
Top Factors Impacting World COPD and Asthma Devices Market 2015-2022
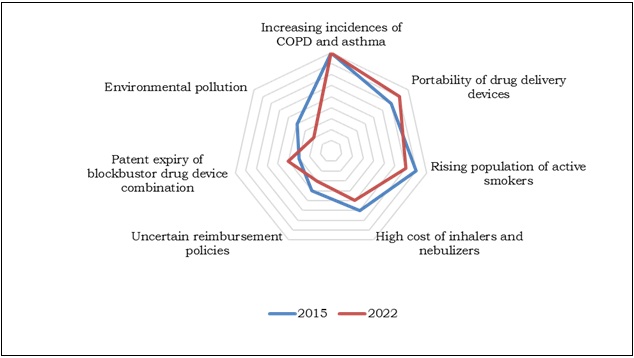
Global COPD & Asthma Devices Market, By Product
Inhalers
Nebulizers
Inhalers accounted for the major market and is expected to continue its dominance till 2020
Global COPD & Asthma Devices Market, By Geography
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
LAMEA
LAMEA region would exhibit the highest CAGR of 4.9% during 2017-2020
Conference Highlights
- Pathogenesis of COPD
- CO-Morbidities in COPD
- Epidemology of COPD
- COPD Theraupetics
- COPD Exacerbations
- Self-Management and Prevention of COPD
- Management of COPD
- Diagnostic Evaluation of COPD
- Lung Diseases
- Airway and Therapeutic Devices
- Pediatric Pulmonary,Critical care and Sleep
- Asthma and allergy
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Cardiovascular Risk and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Lung cancer
- Pulmonary diseases-treatment and therapies
- Environmental and Occupational lung Disease
- Lung Transplantation
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | May 17-18, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Medicine
- Journal of Lung Diseases & Treatment
- Journal of Pulmonary Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by